编者按:来自意大利米兰的欧洲肿瘤研究所(IEO)和意大利人类研究医院(humanitas research hospital)的Giulia Veronesi医生的讲题“生物标志物是否有助于肺小结节诊断(Can biomarkers be of help in the diagnosis)”,设置在16日日程的“小结节的诊断带来的挑战(The diagnostic challenge of small nodules)”这一环节。生物标志物是一个热门话题,那么生物标志物对肺小结节的诊断有无帮助呢?为此《肿瘤瞭望》记者采访了Veronesi医生。
生物标志物是否有助于肺小结节诊断?低剂量CT扫描已被证实为有效的肺癌筛查工具,但低剂量CT扫描的缺点之一是假阳性率高,有很大部分的结节性质不确定。因此,需要更好的工具验证结节的性质,因此分子标志物的研究非常重要,目前研究者已经分析了一些可能有效的标志物。
其中,有两类循环标志物被证明有效:①补体裂解产物(complement split product)c4d水平检测有助于肺癌诊断,但研究证明其缺点是灵敏度低,因此不是最有前景的标志物之一。②自身抗体可作为肺癌早诊的标志物,研究人员对7种自身抗体(CAGE/ GBU 4-5/HER2/ p53/ c0myc/ NY-ES0-1/MUC1)进行验证,但这种方法检出率很低,敏感度约为40%,而特异性非常高(表1)。
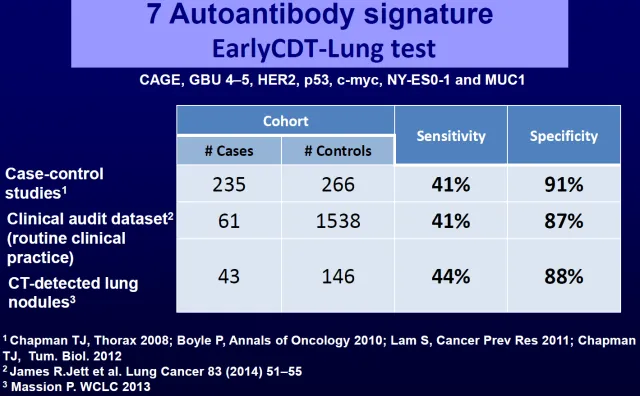
表1
最有前景的生物标志物是血清和血浆中的循环miRNA分子。研究者已经确认了由13个miRNA组成的标志物,对患者进行CT扫描和血液标本miRNA分析(图1)。13 miRNA检测(13 miRNA Test)被用于肺小结节的诊断,目前正在进行一个多中心、前瞻性肺癌筛查研究。
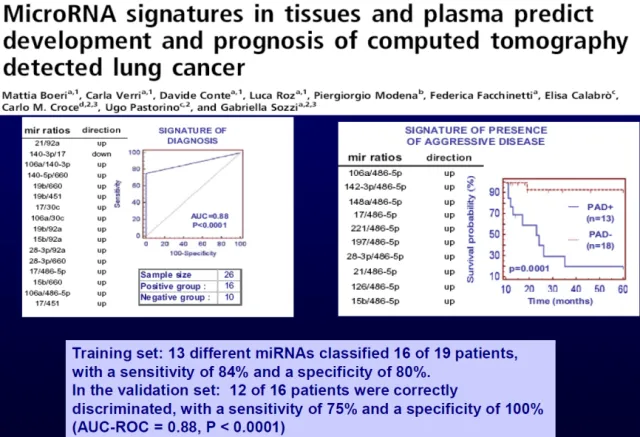
图1.
根据Veronesi医生报告,目前研究者已发现诸多肿瘤标志物,其中很少能达到可接受的灵敏度和特异性;目前前瞻性研究正在对两个有前景的血清和血浆中miRNA标志物进行评估;miRNA分析和PET扫描联合是一种有前景的检测方法,可降低检出小结节的假阳性率、增加诊断灵敏度,但还需要进一步研究检验;还没有可应用于临床实践、诊断小结节的分子检测方法。
如何提高肺小结节的诊断准确性?
提高肺小结节诊断的准确性是肺癌筛查的重要目标。在诊断流程应考虑各种相关参数以求诊断精确,如体积倍增时间(VDT)、CT和PET检测结果,结节大小,结节形状等。随着经验的增加,假阳性检出率不断降低。如果肺小结节诊断阳性,则组织跨多学科小组进行讨论,以最大程度地提高诊断准确性。
恶性孤立性肺结节(SPN)的最佳管理策略?
对于适合手术的患者来说标准治疗是手术治疗。肺癌微创手术的应用越来越普遍,电视胸腔镜手术或机器人手术的方法可减少手术创伤,提高患者的生活质量。肺癌手术的另一种发展趋势是切除范围减少。过去标准术式是肺叶切除术及彻底淋巴结清扫。而Veronesi医生的研究中,结节很小的早期肺癌患者大多行微创亚肺叶切除术,大多数情况下肺段切除术(anatomic segmentectomy)的效果已经很好。而大于2厘米或侵袭性强的肿瘤行标准肺叶切除术(微创手术)。
研究者将评估立体定向放射治疗各种肺小结节患者(原发肺癌、多灶性肺癌、第二原发肺癌,或已行肺叶切除术的患者)的效果。对于不适宜手术的肺小结节患者,放疗是很好的替代治疗方式。目前,研究者对放疗与手术(针对适用手术的患者)的疗效进行比较,但手术与较多并发症相关。未来研究方向是改进肺癌筛查,进行无创性诊断和无创性治疗。
访谈原文
Oncology Frontier: I?have just listened your excellent report “Can biomarkers be of help in the diagnosis of small nodules?” Could you please talk more about this question?
《肿瘤瞭望》:我刚才听了您的精彩报告“生物标记物是否有助于肺小结节诊断?”你能再谈谈这个问题吗?
Dr. Veronesi: Thank you very much for the invitation. I am a thoracic surgeon, and I have dedicated many years to the screening of lung cancer. I am involved in the research where the objective is to identify molecular markers for early detection of lung cancer. I was asked to give the presentation yesterday, and I reviewed all the diagnostic signatures. We have an advanced phase of validation which is of help in the diagnosis of small lung cancer, small nodules. As you know, screening has been validated as a tool with low-dose CT scan for lung cancer, but one of the drawbacks is the high rate of indeterminate nodules in screening. So it’s important to have tools to better characterize these nodules, and the research of molecular markers is very important in this regard. A number of signatures have been analyzed.
Veronesi: 博士:我是一名胸外科医生,多年致力于肺癌筛查。目前我所参与的一项研究致力于确认可早期发现肺癌的分子标志物。我被邀请在ELCC 16日的议程中展示研究结果,报告中我对所有的诊断标志物进行了回顾。低剂量CT扫描已被证实为有效的肺癌筛查工具,但低剂量CT扫描的缺点之一是假阳性率高,有很大部分的结节性质不确定。因此,需要更好的工具验证结节的性质,因此分子标志物的研究非常重要,目前研究者已经分析了一些可能有效的标志物。
There are two categories of circulating markers, which are very good phases of validation. One is an immunity component of the complement in this molecule, the C4D, which has been detected by a group of Spanish researchers. It is a good tool, but it is already validated in the screening court with the main limitation of low sensitivity. So, it is not one of the most promising. Another tool is the research of autoantibodies, against abnormal partings in the surface of cancer cells. There is a signature of seven autoantibodies that is already put on the market, yet the detection rate is very low, around 40% sensitivity, while the specificity is very high.
其中,有两类循环标志物被证明有效:①补体裂解产物(complement split product)c4d水平检测有助于肺癌诊断,但研究证明其缺点是灵敏度低,因此不是最有前途的标志物之一。②自身抗体可作为肺癌早诊的标志物,有7种自身抗体(CAGE/ GBU 4-5/HER2/ p53/ c0myc/ NY-ES0-1/MUC1)已经上市,但这种方法检出率很低,敏感度约为40%,而特异性非常高(表1)。
So, the two most promising markers are a group of molecular circulating micro-RNAs, which we have worked on molecules in the serum. We have identified a signature of 13 micro-RNAs, detected in a screening court, validated in retrospect in a second screening court, and now there is an ongoing study, a prospective screening trial,multicenter, with the main objective of validating the prospect of this type of signature. The accuracy is around 80%, and we perform a CT scan and a blood sample with a micro-RNA analysis. The objective of this new study, that involves 7,000 individuals in Italy, is to obtain a molecular marker able to reduce the need of a CT scan, thus improving the effectiveness of screening, because CT scans have drawbacks such as exposure to radiation. So, this can be a first line screening tool that can be of help in implementing screening on a large scale population. I think the final validation will be in a prospective randomized trial, so probably we will need an additional five or six years to obtain something that can be used in the clinic.
因此,最有前途的生物标志物是血清和血浆中的循环miRNA分子。研究者已经确认了由13个miRNA组成的标志物,对患者进行13 miRNA检测(13 miRNA Test),目前正在进行一个多中心、前瞻性肺癌筛查研究,通过CT扫描和血液标本miRNA分析,精准度达80%左右。该研究在意大利入组7000名患者,主要研究目的是对以上标志物进行验证。这种检测方法可减少CT扫描的需要,提高肺癌筛查率(因为CT扫描有缺点如辐射),可作为一线工具实施大规模筛查。这种方法还需前瞻性随机试验的验证,若应用于临床还需等待5、6年。其他非循环标志物还有经皮生物电导(transcutaneous bioconductance)、痰细胞3D、呼吸检测(breath test)。





 京公网安备 11010502033352号
京公网安备 11010502033352号